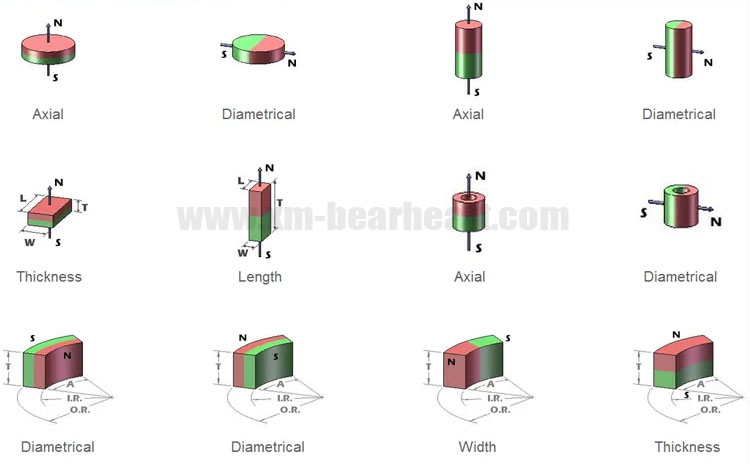
What are the directions of magnetization? How to magnetize a magnet?
What is the direction of magnetization?
The magnetization direction is the first step for permanent magnet materials such as NdFeB and SmCo magnets to obtain magnetism. It represents the position of the north and south poles in a magnet or magnetic assembly. The magnetism of permanent magnet materials mainly comes from its easily magnetizable crystal structure. Due to this structure, the magnet can obtain very high magnetic properties under the action of a strong external magnetic field, and its magnetic properties will not disappear after the external magnetic field disappears.
Can the magnetization direction of a magnet be changed?
From the perspective of magnetization direction, magnetic materials are divided into two categories: isotropic magnets and anisotropic magnets. As the name suggests:
Isotropic magnets have the same magnetic properties in any direction and attract together arbitrarily.
Anisotropic permanent magnetic materials have various magnetic properties in different directions, and the direction in which they can obtain the best/strongest magnetic properties is called the orientation direction of permanent magnetic materials.
Orientation technology is a necessary process for producing anisotropic permanent magnet materials. The new magnets are anisotropic. The magnetic field orientation of powder is one of the key technologies for manufacturing high-performance NdFeB magnets. Sintered NdFeB is generally pressed by magnetic field orientation, so the orientation direction needs to be determined before production, which is the preferred magnetization direction. Once a neodymium magnet is made, it cannot change the direction of magnetization. If it is found that the magnetization direction is wrong, the magnet needs to be re-customized.
What is the difference between axial magnetization and radial magnetization of a magnet?
Axial magnetization and radial magnetization are commonly used to indicate the magnetization direction of cylinder/disc, ring and arc magnets. For axially magnetized magnets, the magnetic force is mainly on the two end faces. For radially magnetized magnets, the magnetic field is mainly on the inner and outer arcs.
What is magnetization?
Magnetization is the process of applying a magnetic field to the permanent magnet material along the direction of the magnetic field orientation and gradually increasing the magnetic field strength to reach the technical saturation state.
Sintered NdFeB permanent magnet materials can be made into square, cylindrical, circular, arc and other forms. Their magnetization direction is relatively simple, generally axial and radial magnetization.
In addition to the simple magnetization direction, the sintered NdFeB ring can also be multi-pole magnetized according to actual needs, that is, multiple N poles and S poles can be displayed on one plane after magnetization. Multi-pole rings require the use of specially designed magnetizing fixtures, thus incurring additional magnetizing fixture costs.
How to magnetize a magnet?
A magnetizer is a tool for magnetizing magnetic materials or components. Through it, we can apply a magnetic field to permanent magnet products that need to be magnetized.
The basic principle of magnetization is to place a magnetizable object to be magnetized in a magnetic field formed by a coil through which a direct current flows. There are two ways: DC magnetization and pulse magnetization.
If the magnetization field does not reach the technical saturation field, the remanence Bj and coercive force Hcj of the permanent magnet material will not reach their proper values. In this case, how to determine the energy of the magnetizer?
First, determine the size of the magnetized tool according to the size of the magnetized product and the direction of magnetization. The magnitude of the magnetic field at the center of the tool is then calculated. The size of the tool magnetic field should be 3-5 times the coercive force of the magnet. Then calculate the magnetizing current. According to the current and voltage of the magnetizer, the capacity of the energy storage capacitor of the magnetizer is finally determined.
