What is a Neodymium Iron Boron Magnet?
What is a neodymium iron boron magnet?
A neodymium magnet (also known as NdFeB, NIB or Neo magnet) is the most widely used type of rare-earth magnet. It is a permanent magnet made from an alloy of neodymium, iron, and boron to form the Nd2Fe14B tetragonal crystalline structure. Developed independently in 1984 by General Motors and Sumitomo Special Metals, neodymium magnets are the strongest type of permanent magnet available commercially.Because of different manufacturing processes, they are divided into two subcategories, namely sintered NdFeB magnets and bonded NdFeB magnets. They have replaced other types of magnets in many applications in modern products that require strong permanent magnets, such as electric motors in cordless tools, hard disk drives and magnetic fasteners.
Quick links to Neodymium Magnets Information:
What is the composition of neodymium permanent magnet materials?
The NdFeB permanent magnet material is a permanent magnet material based on the intermetallic compound Nd2Fe14B. The main components are rare earth elements neodymium (Nd), iron (Fe), and boron (B). The third-generation rare earth permanent magnet NdFeB is the most powerful permanent magnet in contemporary magnets. Its main raw material is 29% rare earth metal neodymium -32.5% metal element iron 63.95-68.65% non-metal element boron 1.1-1.2% add dysprosium 0.6-8% niobium 0.3-0.5% aluminum 0.3-0.5% copper 0.05-0.15% and other elements.
What are the characteristics Neodymium magnets?
· Very high resistance to demagnetization
· High energy for size
· Good in ambient temperature
· Material is corrosive and should be coated for long term maximum energy output
· Low working temperature for heat applications, but higher levels of heat resistance materials are being introduced periodically
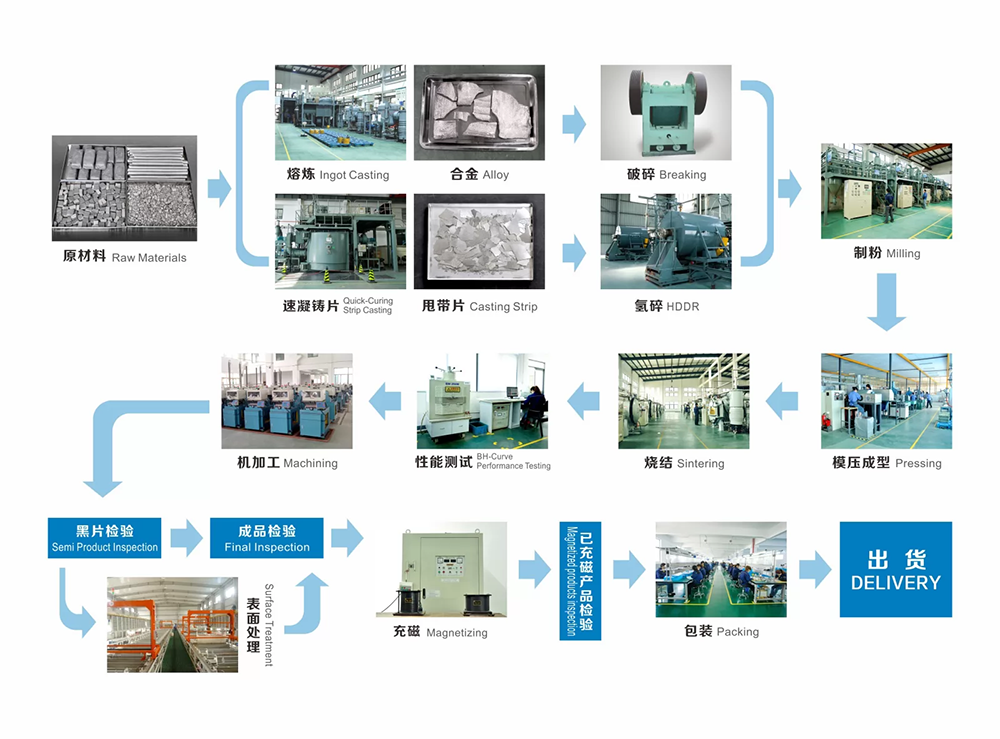
How neodymium magnets are made?
Technological process: ingredients → smelting ingot/spinning → powder making → profiling → sintering and tempering → magnetic inspection → grinding → pin cutting → electroplating → finished product. Among them, ingredients are the basis, and sintering and tempering is the key step.
Magnetic Properties of Sintered Neodymium Magnets
Series | Grade | Remanence | Coercive Force | Intrinsic Coercive force | Max. Energy Product | Max.Working Temp. | |||||
Br | Hcb | Hci | (BH) max | L/D=0.7 | |||||||
T | kGs | KA/m | KOe | KA/m | KOe | KJ/m3 | MGOe | ºC | °F | ||
N | N35 | 1.17-1.24 | 11.7-12.4 | ≥860 | ≥10.8 | ≥955 | ≥12 | 263-295 | 33-37 | 80 | 176 |
N38 | 1.22-1.30 | 12.2-13.0 | ≥860 | ≥10.8 | ≥955 | ≥12 | 287-318 | 36-40 | 80 | 176 | |
N40 | 1.26-1.32 | 12.6-13.2 | ≥860 | ≥10.8 | ≥955 | ≥12 | 302-334 | 38-42 | 80 | 176 | |
N42 | 1.29-1.35 | 12.9-13.5 | ≥860 | ≥10.8 | ≥955 | ≥12 | 318-350 | 40-44 | 80 | 176 | |
N45 | 1.32-1.38 | 13.2-13.8 | ≥860 | ≥10.8 | ≥955 | ≥12 | 334-366 | 42-46 | 80 | 176 | |
N48 | 1.37-1.43 | 13.7-14.3 | ≥836 | ≥10.5 | ≥876 | ≥11 | 358-390 | 45-49 | 80 | 176 | |
N50 | 1.40-1.45 | 14.0-14.5 | ≥836 | ≥10.5 | ≥876 | ≥11 | 374-406 | 47-51 | 80 | 176 | |
N52 | 1.42-1.48 | 14.2-14.8 | ≥836 | ≥10.5 | ≥876 | ≥11 | 390-422 | 49-53 | 80 | 176 | |
N54 | 1.45-1.51 | 14.5-15.1 | ≥836 | ≥10.5 | ≥876 | ≥11 | 398-438 | 50-55 | 80 | 176 | |
M | N35M | 1.17-1.24 | 11.7-12.4 | ≥860 | ≥10.8 | ≥1114 | ≥14 | 263-295 | 33-37 | 100 | 212 |
N38M | 1.22-1.30 | 12.2-13.0 | ≥915 | ≥11.5 | ≥1114 | ≥14 | 287-318 | 36-40 | 100 | 212 | |
N40M | 1.26-1.32 | 12.6-13.2 | ≥939 | ≥11.8 | ≥1114 | ≥14 | 302-334 | 38-42 | 100 | 212 | |
N42M | 1.29-1.35 | 12.9-13.5 | ≥955 | ≥12.0 | ≥1114 | ≥14 | 318-350 | 40-44 | 100 | 212 | |
N45M | 1.32-1.38 | 13.2-13.8 | ≥987 | ≥12.4 | ≥1114 | ≥14 | 334-366 | 42-46 | 100 | 212 | |
N48M | 1.37-1.43 | 13.7-14.3 | ≥1019 | ≥12.8 | ≥1114 | ≥14 | 358-390 | 45-49 | 100 | 212 | |
N50M | 1.40-1.45 | 14.0-14.5 | ≥1043 | ≥13.1 | ≥1114 | ≥14 | 374-406 | 47-51 | 100 | 212 | |
N52M | 1.42-1.48 | 14.2-14.8 | ≥1059 | ≥13.3 | ≥1114 | ≥14 | 390-422 | 49-53 | 100 | 212 | |
H | N35H | 1.17-1.24 | 11.7-12.4 | ≥876 | ≥11 | ≥1350 | ≥17 | 263-295 | 33-37 | 120 | 248 |
N38H | 1.22-1.30 | 12.2-13.0 | ≥915 | ≥11.5 | ≥1350 | ≥17 | 287-318 | 36-40 | 120 | 248 | |
N40H | 1.26-1.32 | 12.6-13.2 | ≥939 | ≥11.8 | ≥1350 | ≥17 | 302-334 | 38-42 | 120 | 248 | |
N42H | 1.29-1.35 | 12.9-13.5 | ≥963 | ≥12.1 | ≥1350 | ≥17 | 318-350 | 40-44 | 120 | 248 | |
N45H | 1.31-1.37 | 13.1-13.7 | ≥979 | ≥12.3 | ≥1350 | ≥17 | 335-366 | 42-46 | 120 | 248 | |
N48H | 1.37-1.43 | 13.7-14.3 | ≥1011 | ≥12.7 | ≥1274 | ≥16 | 358-390 | 45-49 | 120 | 248 | |
N50H | 1.40-1.45 | 14.0-14.5 | ≥1027 | ≥12.9 | ≥1274 | ≥16 | 374-406 | 47-51 | 120 | 248 | |
SH | N33SH | 1.14-1.21 | 11.4-12.1 | ≥852 | ≥10.7 | ≥1592 | ≥20 | 247-279 | 31-35 | 150 | 302 |
N35SH | 1.17-1.24 | 11.7-12.4 | ≥876 | ≥11 | ≥1592 | ≥20 | 263-295 | 33-37 | 150 | 302 | |
N38SH | 1.22-1.29 | 12.2-12.9 | ≥915 | ≥11.5 | ≥1592 | ≥20 | 287-318 | 36-40 | 150 | 302 | |
N40SH | 1.26-1.32 | 12.6-13.2 | ≥939 | ≥11.8 | ≥1592 | ≥20 | 302-334 | 38-42 | 150 | 302 | |
N42SH | 1.29-1.35 | 12.9-13.5 | ≥963 | ≥12.1 | ≥1592 | ≥20 | 318-350 | 40-44 | 150 | 302 | |
N45SH | 1.32-1.38 | 13.2-13.8 | ≥994 | ≥12.5 | ≥1592 | ≥20 | 335-366 | 42-46 | 150 | 302 | |
UH | N30UH | 1.08-1.16 | 10.8-11.6 | ≥812 | ≥10.2 | ≥1990 | ≥25 | 223-255 | 28-32 | 180 | 356 |
N33UH | 1.14-1.21 | 11.4-12.1 | ≥852 | ≥10.7 | ≥1990 | ≥25 | 247-279 | 31-35 | 180 | 356 | |
N35UH | 1.17-1.24 | 11.7-12.4 | ≥876 | ≥11 | ≥1990 | ≥25 | 263-295 | 33-37 | 180 | 356 | |
N38UH | 1.22-1.29 | 12.2-12.9 | ≥915 | ≥11.5 | ≥1990 | ≥25 | 287-318 | 36-40 | 180 | 356 | |
N40UH | 1.26-1.32 | 12.6-13.2 | ≥939 | ≥11.8 | ≥1990 | ≥25 | 302-334 | 38-42 | 180 | 356 | |
N42UH | 1.29-1.35 | 12.9-13.5 | ≥963 | ≥12.1 | ≥1990 | ≥25 | 318-350 | 40-44 | 180 | 356 | |
EH | N30EH | 1.08-1.15 | 10.8-11.5 | ≥812 | ≥10.2 | ≥2388 | ≥30 | 223-255 | 28-32 | 200 | 392 |
N33EH | 1.14-1.21 | 11.4-12.1 | ≥851 | ≥10.7 | ≥2388 | ≥30 | 247-279 | 31-35 | 200 | 392 | |
N35EH | 1.17-1.24 | 11.7-12.4 | ≥876 | ≥11 | ≥2388 | ≥30 | 263-295 | 33-37 | 200 | 392 | |
N38EH | 1.22-1.29 | 12.2-12.9 | ≥915 | ≥11.5 | ≥2388 | ≥30 | 287-318 | 36-40 | 200 | 292 | |
AH | N28AH | 1.04-1.12 | 10.4-11.2 | ≥772 | ≥9.70 | ≥2786 | ≥35 | 207-239 | 26-30 | 230 | 446 |
N30AH | 1.08-1.15 | 10.8-11.5 | ≥812 | ≥10.2 | ≥2786 | ≥35 | 223-255 | 28-32 | 230 | 446 | |
N33AH | 1.14-1.21 | 11.4-12.1 | ≥852 | ≥10.7 | ≥2786 | ≥35 | 247-279 | 31-35 | 230 | 446 | |
The above-mentioned data of magnetic properties and physical properties are given at room temperature.
The max working temperature of magnet is changeable due to length-diameter ratio, coating thickness and other environment factors.
Other Properties of Sintered Neodymium Magnets
Items | Parameters | Unit | Reference Range |
Other Magnetic Properties | Temper. Coeff. of Br / α(Br) | %/℃ | -0.08 ~ -0.13 |
Temper. Coeff. of Br / β(Hcj) | %/℃ | -0.35 ~ -0.80 | |
Curie Temperature / Tc | ℃ | 310-380 | |
Recoil Permeability / μrec | – | 1.05 | |
Physical Properties | Density / ρ | g/cm3 | 7.40-7.80 |
Vickness Hardness / HV | – | 550-650 | |
Electrical Resistivity | μΩ·m | 1.4 | |
Compressive Strength | MPa | 1050 | |
Tensile Strength | MPa | 80 | |
Bending Strength | MPa | ||
Thermal Conductivity | W/(m·K) | 6-8 | |
Coeff. of Thermal Expansion | 10-6/K | C⊥: -1.5, C∥6.5. |
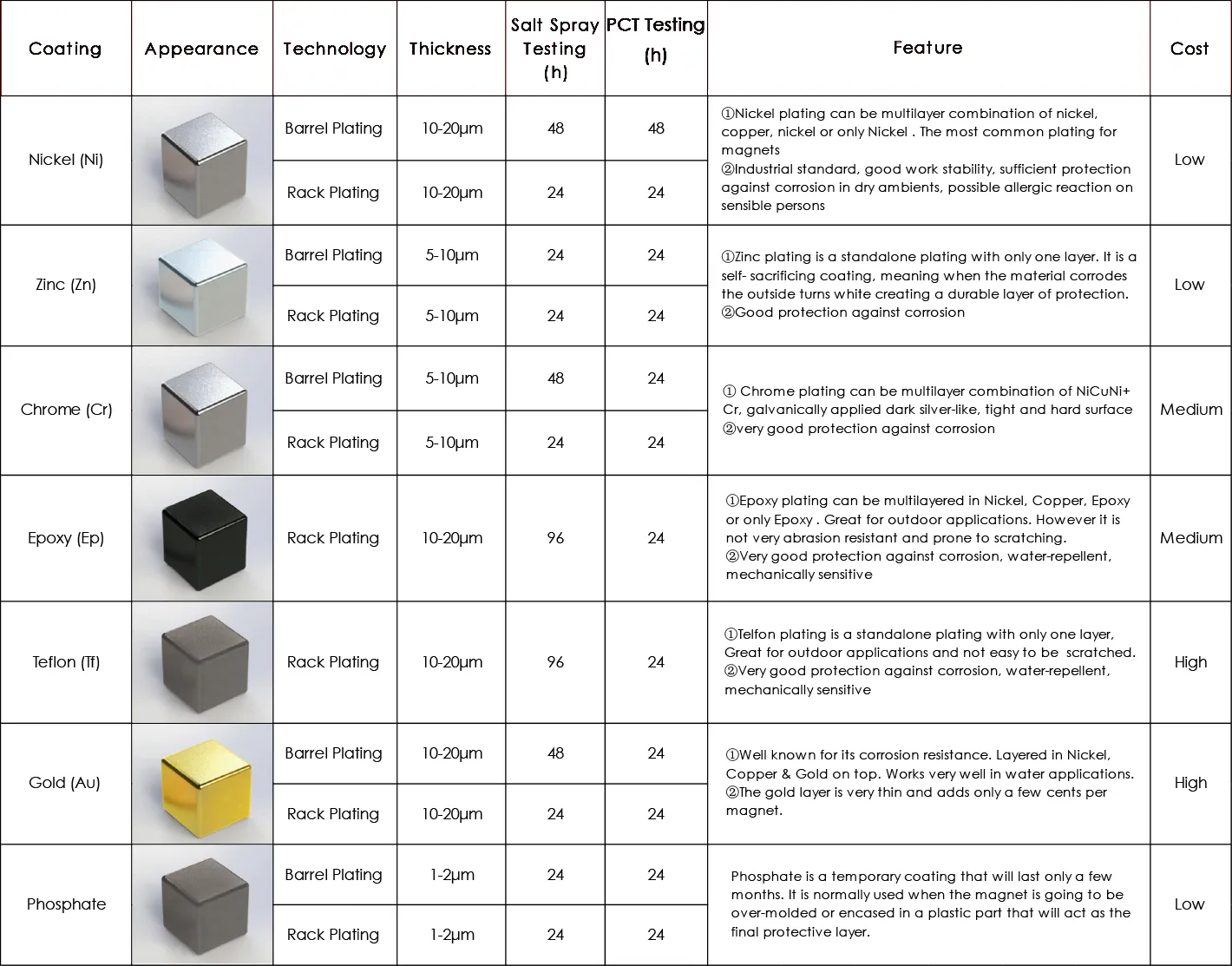
Surface Treatment of Sintered Neodymium Magnets
Surface protective treatment is the ineluctable procedure for the sintered Neodymium magnets. Nd-rich phase exhibit quite strong oxidation tendency and will form a primary battery system with main phase under humid condition. Finally, Nd-rich phase is corroded and main phase particle peeled from the body gradually. Surface protective treatment of sintered Neodymium magnets is can be divided into wet and dry process. The commonly-used wet process includes electroplating, electrolessplating, electrophoresis, spray coating, and dip coating. Dry process includes physical vapor deposition (PVD) process and chemical vapor deposition (CVD) process.
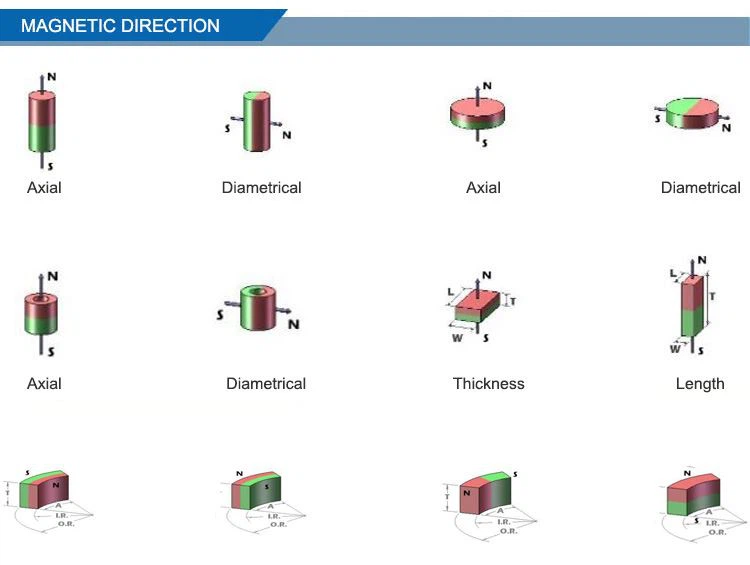
Magnetic direction of Sintered Neodymium Magnets
Magnetization process refers to apply magnetic field along the definite direction of the permanent magnet to saturate the magnet. Different permanent magnet requires unlike magnetic field strength to achieve saturation. As a type of anisotropic magnet, sintered Neodymium magnets have a preferred direction of magnetization and various pole configurations can be realized as long as not conflicting with its own orientation.
Applications of Neodymium Magnets
Neodymium magnets have replaced Alnico and ferrite magnets in many applications where strong permanent magnets are required, because their greater strength allows the use of smaller, lighter magnets. These applications include:
· package closures/ displays and signs/ head actuators for computer hard disks/ magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)/ magnetic guitar pickups
· loudspeakers and headphones/ magnetic bearings and couplings/ permanent magnet motors/ cordless tools/ servo motors/lifting and compressor motors
· synchronous motors/ spindle and stepper motors/ electrical power steering/ drive motors for hybrid and electric vehicles/ actuators